Python Class with Advait
#variables are used to store some values
var1 = 50
var2 = 100
print(var1 + var2)
var1 = 500
var2 = 100
print(var1 + var2)
#Basic
#datatypes: str, int, float, bool, complex
var1 = "HELLO" # str - you have the value in quoation
print(type(var1))
var1 = 100 #without any decimal part - integer(int)
print(type(var1))
var1 = 100.0 #float value
print(type(var1))
var1 = True #bool - False
print(type(var1))
var1 = 5j #complex (python)=imaginary (maths)
var2 = var1 * var1 #implicit conversion into complex since var1 is also complex
print(var2)
print(type(var1))
#
var1 = 100
var2 = 3.5
var3 = var1 + var2 #implicit conversion into float since var2 is a float
print()
str1 = "55"
str1 = int(str1) #explicit conversion
#int(), str(), float(), bool(), complex()
var1 = 0;var1 = bool(var1);print(var1); #False - bool
var1 = "";
var1 = bool(var1);
print(var1) ; #False - bool
len = float(input("Enter length of the rectangle: "))
breadth = float(input("Enter breadth of the rectangle: "))
area = len * breadth
print("Area of the rectangle is ",area)
print(f"Rectangle with length = {len} and breadth = {breadth} has an area of {area:.1f}")
player = "Imbababonbeta"
country = "Zimbabwe"
position = "wicket-keeper"
print(f"Player {player:<16} plays for {country:^10} and is {position:>15} of the team")
player = "Rohit"
country = "India"
position = "captain"
print(f"Player {player:<16} plays for {country:^10} and is {position:>15} of the team")
#Player Imbababonbeta plays for Zimbabwe and is wicket-keeper of the team
#Player Rohit plays for India and is captain of the team
########
## OPERATORS
### ARITHMETIC OPERATORS: + - * /
## input values have to be numeric (int, float, complex)
var1 = 50
var2 = 20
print(var1 + var2)
print(var1 - var2)
print(var1 * var2)
print(var1 / var2)
# ** power, 5 ** 4 => 5 * 5 * 5 * 5
print(var1 ** var2) # 50 to the power of 20
# how to find square root of 21 ?
print(21 ** 0.5) #4.58257569495584
#cube root of 21 =
print(21 ** (1/3))
# // - integer division
print(10 / 3)
print("Integer Division = ",10 // 3)
# % Modulo - remainder
#20 / 3 = 6 + 2/3
print(20 % 3)
print(50 % 30) # 20 is remainder
# Comparison operators: compare the values (bigger/smaller)
# input as numeric and output is BOOL
var1 = 15
var2 = 25
print(var1 > var2) #false

#Arithematic operations: + - * / , **, // and % (modulo)
## input as numbers and output was numbers
#Comparison operators: input are the numbers / output - bool
# > >= < <= == !=
val1 = 30
val2 = 40
val3 = 30
print(val1 > val2) #is leftside val greater than rightside value?
print(val1 > val3) #False
print(val1 >= val3) #is val1 greater than or equal to? - True
print(val1 < val2) #
print(val1 <= val3) #
print(val1 == val3) # == is for asking question, are they equal?
print(val1 == val2) #False
print(val1 != val3) #False
print(val1 != val2) #True
#bool operators - Logical operators : Input and Output- bool
#Prediction 1: Sachin and Laxman are going to do this job - F
#Prediction 2: Sachin or Laxman are going to do this job - T
#Actual: Sachin and Rahul did the job
#AND - even one False will make output False
#OR - even one TRUE will make output True
#NOT - opposite
val1 = 30
val2 = 40
val3 = 30
print("==>: ",val1 > val2 or val1 > val3 and val1 >= val3 or
val1 < val2 and val1 <= val3 or val1 == val3 and val1 == val2 or
val1 != val3 or val1 != val2)
#T
#membership operator - in
print(5 in [2,4,5,6,8])
#bitwise operator - works by converting the numbers to boolean
# binary equivalent of 33 ?
print(bin(33)) #0b100001
print(int(0b101111011111))
# and (&) or (|) >> (right shift) << (left shift)
print(22 & 33) #0
print(33 & 22) #0
print(bin(33), bin(22))
## 33 = 100001
## 22 = 010110
## (&) 000000
## (|) 110111
print(int(0b110111)) #55
print(33 | 22) # 55
##
print(55 >>2)
# 55 = 110111 >> 1 = 11011 >> 1 = 1101
print(int(0b1101)) #13
print(55 << 2) # 110111 << 1 = 1101110 << 1 = 11011100
###
# if - checking conditions
val1 = 30
if val1 > 0:
print("Value is positive")
print("Positive Positive Positive")
print("Thank you for using my program")
# 300 pts
## ? 300
print("You win")
print("You lose")
print("Tied")
#TUPLE - immutable version of List
str1 = "hello"
str2 = 'Good evening' \
'How are you?'
str3 = '''Hello there
hope you are doing good
we shall meet soon'''
str4 = """I am fine
how are you"""
print(str2)
print(str3)
print(type(str1))
#functions (global) v methods (belong to a class)
str1 = "hello"
print(str1.islower())
print(str1.isupper())
#isdigit()
val1 = input("Enter length of the rectangle: ")
if val1.isdigit():
val1 = int(val1)
print(val1)
else:
print("Sorry, this is not a valid number")
name1 = "Sachin Tendulkar"
print(name1.isalpha())
txt1 = "hello@123"
print(txt1.isalnum())
###
str1 = "HellOOO how are YOU?"
print(str1.lower())
#### Build a game - guessing number ####
import random
num = 55
attempt = 0
low,high = 1,100
while True:
#guess = int(input("Enter the number: "))
guess = random.randint(low, high)
attempt+=1
if guess ==num:
print(f"You got it in {attempt} attempts!")
break
elif guess > num:
print(f"Hint: Your value {guess} is higher")
high=guess-1
else:
print(f"Hint: Your value {guess} is lower")
low=guess+1
str1 = "Hello"
print(str1[-1] , str1[len(str1)-1])
print(str1[1])
print("Length = ",len(str1))
# range(a,b,c) - a=initial value, b = ending value, c=increment
# range(2,14,3) - 2,5,8,11
print(str1[0:4], str1[:4])
print(str1[-5:-1], str1[:-1])
# llo
print(str1[2:5], str1[2:])
print(str1[-3:])
vowel_count = 0
str1 = "This is a Sample STATEMENT to test"
for i in str1:
#print("Hello: ",i)
if i in 'aeiouAEOIU':
vowel_count+=1
print(f"Total vowels in '{str1}' is {vowel_count}")
# strings are immutable
str1 = "Hello"
str1=str1[0]+'E'+str1[2:]
print("New str1 = ", str1)
str2 = "This is a Sample STATEMENT to test"
str3="This,is,a,sample,text2,work,on,it"
output1 = str2.split()
output1 = str3.split(',')
print(output1)
print(str2)
print("Index: ",str2.index('i',3,len(str2)))
str4='abcd abc ab a'
#find all indices of b
tot = str4.count('ab')
print("Total bs = ",tot)
srt = 0
for i in range(3):
print(str4.index('ab',srt))
srt=str4.index('ab',srt)+1


### LIST: linear ordered mutable collection
l1 = []
print(type(l1))
l1=[3,"Hello",False,5.0, [2,4,6]]
l1.append(45)
#collection - stores multiple values with single variable name
#List, Tuple, Dictionary and Set
#List - linear collection
l1 = [5,"Hello",False,[4,8,12]]
print(type(l1)) #<class 'list'>
#accessing (similar to strings)
print(l1[1][0])
print(type(l1[1]))
print(l1[-1][1])
l2 = [5.6,"Good Evening"]
print(l1+l2)
print(l2 * 3)
l3=[-1]*10
print(l3)
for i in l1:
print(i)
for i in range(len(l1)):
print(l1[i])
l4=[]
#read the value from the user and if its number only then add to this list
val1 = input("Enter a number: ")
if val1.isdigit():
l4.append(int(val1))
print("After first step, L4 looks like: ",l4)
l5 = []
l5.append(100)
l5.append(200)
l5.insert(1,300) # takes- pos, value
l5.insert(1,400)
print("After addition: ",l5)
l5.pop(2) #input as position(index)
l5.remove(200) #takes values as input
print(l5)
### Stack & Queue ##
## Stack - LIFO data structure
stack=[]
while True:
print("Enter your options: ")
print("1. Display Your Stack")
print("2. Add a member to the stack")
print("3. Remove a member from the stack")
print("4. Exit")
ch=input("Choice : ")
if ch=="1":
print("Content of the stack is:\n",stack)
elif ch=="2":
pass
elif ch=="3":
pass
elif ch=="4":
break
else:
print("Sorry I dont understand you, try again!")
# Queue: First element added is the first one to go - FIFO (First In First Out)
l6 = [100,200,300,400,100,200,300,100,200,100]
print(l6.index(100)) #element
print(l6.index(100, 2)) # element with start position
print(l6.index(100, 5,8)) # element with start and end pos
print("count = ",l6.count(200))
#Deep and Shallow copy
l7 = l6 #Deep copy - 2 names for same set of values
l8 = l6.copy() #creates a duplicate copy -
print("1. L6 = ",l6)
print("1. L7 = ",l7)
print("1. L8 = ",l8)
l6.append(500)
l7.append(600)
l8.append(700)
print("2. L6 = ",l6)
print("2. L7 = ",l7)
print("2. L8 = ",l8)
# list is linear ordered mutable collection
l6[0] = 110 #edit the value unlike string
print(l6)
l7 = [2,4,6,8,10]
print(l6+l7) #l6 and l7 retains original values
l6.extend(l7) #l6 will get l7 values
print(l6)
print("Before Reverse: ",l6)
l6.reverse()
print("After Reverse: ",l6)
l6.sort()
print("After Sort: ",l6)
l6.sort(reverse=True)
print("After Reverse Sort: ",l6)
l6.clear()
print("Last: ",l6)
str1 = "HELLO HOW ARE YOU"
print(str1.split())
print(str1) #didnt change as it is immutable
l6.append(66)
print(l6) #existing list got changed as it is mutable
#Sequential search
list1 = [12,14,8,6,10,20,4,10,16,18,2]
num = 10
count_num=0
count_index = []
for i in range(len(list1)):
if list1[i]==num:
count_num+=1
count_index.append(i)
print(f"Number of values = {count_num} and indices are: {count_index}")
# Binary Search
list1 = [12,14,8,6,10,20,4,10,16,18,2]
list1.sort()
num = 22
first = 0
last = len(list1)-1
isFound = False
while True:
mid = (first+last) // 2
if list1[mid] ==num:
isFound = True
break
elif list1[mid] <num:
first = mid+1
else:
last = mid-1
if first> last:
break
if isFound:
print("Number is in the list")
else:
print("Number is not in the list")
Q_LIST = ["What is 1+3? (a) 4 (b) 8 (c) 2 (d) 10",
"What is 4+3? (a) 5 (b) 7 (c) 12 (d) 16",
"What is 4*3? (a) 6 (b) 8 (c) 12 (d) 16"]
A_LIST = ["A","B","C"]
import random
q_no = random.randint(0,2)
print("Let's play the Quiz!")
print(Q_LIST[q_no])
inp=input("Your answer please (select a/b/c/d) : ")
if inp.upper() ==A_LIST[q_no]:
print("Congratulations! You win")
else:
print("Sorry, thats not right")
### input: 29 3 2023 output: 29th March 2023
months= ["January","February","March","April","May","June","July","August",
"September","October","November","December"]
date_ending = ['st','nd','rd']+17*['th']+['st','nd','rd'] + 7*['th']+['st']
month_val = 3
print(months[3-1])
date = 21
print(str(date)+date_ending[date-1])
#Tuple - linear ordered immutable collection
t1 = ()
print("type 1 = ",type(t1), len(t1))
t1 = (1,)
print("type 1 = ",type(t1), len(t1))
t1 = (1,2,3,4,1,2,3,1,2,1) #packcing
print("type 1 = ",type(t1), len(t1))
print("4th member - ", t1[3])
print("2s = ",t1.count(2))
print("Position of 3 = ",t1.index(3))
t2 = (2,4,6,8)
a,b,c,d = t2 #unpacking
print(c,d,b,a)
# you can convert tuple to list and list to tuple
t2 = list(t2)
t2 = tuple(t2)
# Tuple like String, is immutable
#advantage is - working with Tuples is faster than reading through a list
##### DICTIONARY
# Dictionary - mutable collection of key-value pair
d1 = {}
print(type(d1))
d1 = {"Advait":[45,34,89,81],"Saurav":[12,42,23,44]}
print(d1["Advait"])
d2 = {False: 45,45:"Cricket","Name": "Sachin",10:"Zeeeero"}
# dictionary should have unique keys
print(d2)
d2.update(d1)
print("After Update: ", d2)
print("Only Keys = ",d2.keys())
print("Only Values = ",d2.values())
print("Only Items = ",d2.items())
for j in d2.keys():
print(j," = " ,d2[j])
print("Printing Items: ")
for i,j in d2.items():
print("Key:",i," & Value: ",j)
# to remove: pop(), popitem()
#popitem removes the last updated KEY (not value)
d3 ={1:"Hello",2:"Hola",3:"Namaste",4:"Bon Jor"}
print("D3 = ",d3)
d3.popitem()
print("After Popitem: ",d3)
d3 ={1:"Hello",2:"Hola",3:"Namaste",4:"Bon Jor",1:"Good Morning"}
print("D3 = ",d3)
d3.popitem()
print("2. After Popitem: ",d3)
d3.pop(1)
print("1. After Pop = ",d3)
actors = {"David":32,"Tim":42,"Rebecca":21,"Mary":45}
male = {"David":"LA","Tim":"NY"}
female = {"Rebecca":"SD","Mary":"WS"}
# David who is a male of 32 years lives in LA
for name in actors.keys():
print_sentence=name +" who is a "
for male_city in male.keys():
if name==male_city:
print_sentence+="male of "+str(actors[name]) +" years lives in "+ male[name]
for female_city in female.keys():
if name==female_city:
print_sentence+="female of "+str(actors[name]) +" years lives in "+ female[name]
print(print_sentence)
# $100 – $57
total_amount = 28
#initially
Rs_5 = 2
Rs_2 = 2
Rs_1 = 2+3 #initial 2 plus change of 3
initial_total = 5*Rs_5 + 2 *Rs_2 + 1*Rs_1
yet_to_be_accounted = total_amount – initial_total
print(“yet_to_be_accounted: “,yet_to_be_accounted)
# 12
Rs_5 += yet_to_be_accounted //5
yet_to_be_accounted%=5
Rs_2 += yet_to_be_accounted //2
yet_to_be_accounted%=2
Rs_1 += yet_to_be_accounted
print(“Total Rs 5 stamps = “,Rs_5)
print(“Total Rs 2 stamps = “,Rs_2)
print(“Total Rs 1 stamps = “,Rs_1)
total_amount = 28
#initially
Rs_5 = 2
Rs_2 = 2
Rs_1 = 2+3 #initial 2 plus change of 3
initial_total = 5*Rs_5 + 2 *Rs_2 + 1*Rs_1
yet_to_be_accounted = total_amount – initial_total
print(“yet_to_be_accounted: “,yet_to_be_accounted)
# 12
Rs_5 += yet_to_be_accounted //5
yet_to_be_accounted%=5
Rs_2 += yet_to_be_accounted //2
yet_to_be_accounted%=2
Rs_1 += yet_to_be_accounted
print(“Total Rs 5 stamps = “,Rs_5)
print(“Total Rs 2 stamps = “,Rs_2)
print(“Total Rs 1 stamps = “,Rs_1)
#SETS
A = {1,5,2,6,9}
B = {6,9,11,14,15}
A.add(5)
print(A)
# LIST, TUPLE, SETS => They can be converted to each others form\
l1 = [2,4,6,8,4,6,8,2,6,8]
l1 = list(set(l1))
print(l1)
#they are returning result as a new set, values of A and B will not change
print(A.union(B))
print(A.intersection(B))
print(A.difference(B))
#___update modifies the main set
A.update(B)
print(A)
print(A.intersection_update(B))
print(A.difference_update(B))
A = {1,5,2,6,9}
B = {6,9,11,14,15}
A.add(5)
print(A)
# LIST, TUPLE, SETS => They can be converted to each others form\
l1 = [2,4,6,8,4,6,8,2,6,8]
l1 = list(set(l1))
print(l1)
#they are returning result as a new set, values of A and B will not change
print(A.union(B))
print(A.intersection(B))
print(A.difference(B))
#___update modifies the main set
A.update(B)
print(A)
print(A.intersection_update(B))
print(A.difference_update(B))
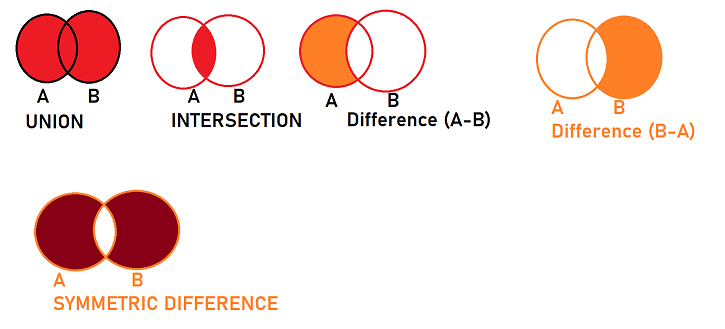
# SET - sets - linear unordered mutable collection - doesnt allow duplicate
set1 = {'Apple','Grapes','Banana','Orange'}
print(type(set1))
set1.add('Cherry')
set2 = {"Pineapple","Mango","Apple","Orange"}
# two ways to remove
set1.remove("Banana")
set1.discard("Apple")
#set1.remove("Rose") - if value isnt there throws error
set1.discard("Rose") #doesnt throw error
print("1. Set1: ",set1)
set1.pop()
set1.update(set2) #union
print("2. Set1: ",set1)
set1.clear()
print("3. Set1: ",set1)
### SET FUNCTIONS ####
set1 = {'Apple','Grapes','Banana','Orange'}
set2 = {"Pineapple","Mango","Apple","Orange"}
#UNION
print("UNION")
print(set1 | set2)
print(set1.union(set2))
print("INTERSECTION")
print(set1 & set2)
print(set1.intersection(set2))
print("DIFFERENCE")
print(set1 - set2)
print(set1.difference(set2))
print(set2 - set1)
print(set2.difference(set1))
print("SYMMETRIC DIFFERENCE")
print(set1 ^ set2)
print(set2 ^ set1)
print(set1.symmetric_difference(set2))
#update() will update the values of main set
# set1.union(set2) - this gives a new set as output
# set1.update(set2) - set1 is updated with the values
# union - update()
set1.update(set2)
print(set1)
# intersection: intersection_update()
set1.intersection_update(set2)
print(set1)
# difference_update()
set1.difference_update(set2)
print(set1)
#symmetric_difference_update()
set1.symmetric_difference_update(set2)
print(set1)
# set, list, tuple => they are inter-convertible
list1 = [3,6,9,12,3,6,9,3,6,3]
list1 = list(set(list1))
print(list1)
set1 = {'Apple','Grapes','Banana','Orange'}
set1 = list(set1)
set1.index("Grapes")
set1 = set(set1)
set1 = tuple(set1)
set1 = set(set1)
print(set1.issubset(set2))
#
list1 = [3,6,9,12,3,6,9,3,6,3]
list2 = [3,6,9,12,15]
#does all the elements of list2 present in list1?
t_list1 =set(list1)
if set(list1).issuperset(set(list2)):
print("yes, list2 value exists in list1")
else:
print("No, list2 has additional elements")
# MAP FILTER REDUCE
#MAP – large set of data and you want to apply same formula over all the values
list1 = [-3,-6,-15,0,5,999,67,34]
#find square of all these values
list2 = []
for i in list1:
list2.append(i*i)
print(list2)
# one line function / lambda function
result = list(map(lambda x:x**2,list1))
print(“Map result = “,result)
# FILTER -used to filter out data from a list based on a condition
# logic of the function in filter should be designed such a way that you get either True or False
result = list(filter(lambda x:x>=0,list1))
print(“Filter result = “,result)
#filter out numbers divisible by 3
result = list(filter(lambda x:x%3==0,list1))
print(“2. Filter result = “,result)
#Reduce
#import functools as ft
from functools import reduce
result = reduce(lambda x,y:(x+y)/2, list1)
print(“3. Result from Reduce: “,result)
# function
def my_qs():
print(“Whats your name?”)
print(“How are you today?”)
print(“Where do you live?”)
my_qs()
#MAP – large set of data and you want to apply same formula over all the values
list1 = [-3,-6,-15,0,5,999,67,34]
#find square of all these values
list2 = []
for i in list1:
list2.append(i*i)
print(list2)
# one line function / lambda function
result = list(map(lambda x:x**2,list1))
print(“Map result = “,result)
# FILTER -used to filter out data from a list based on a condition
# logic of the function in filter should be designed such a way that you get either True or False
result = list(filter(lambda x:x>=0,list1))
print(“Filter result = “,result)
#filter out numbers divisible by 3
result = list(filter(lambda x:x%3==0,list1))
print(“2. Filter result = “,result)
#Reduce
#import functools as ft
from functools import reduce
result = reduce(lambda x,y:(x+y)/2, list1)
print(“3. Result from Reduce: “,result)
# function
def my_qs():
print(“Whats your name?”)
print(“How are you today?”)
print(“Where do you live?”)
my_qs()
# function that doesnt take any input argument nor does it return
def mysum1():
a,b,c=10,20,30
sum=a+b+c
print(“Sum is”,sum)
#function with input arguments
def mysum2(a,b,c): #required positional arguments
print(“A,B and C are: “,a,b,c)
sum=a+b+c
#print(“Sum is”,sum)
return sum
out = mysum2(9,18,27)
print(“Out =”,out)
def mysum1():
a,b,c=10,20,30
sum=a+b+c
print(“Sum is”,sum)
#function with input arguments
def mysum2(a,b,c): #required positional arguments
print(“A,B and C are: “,a,b,c)
sum=a+b+c
#print(“Sum is”,sum)
return sum
out = mysum2(9,18,27)
print(“Out =”,out)
def mysum3(a,b,c=99): #c is default, a & b are required – positional arguments
print(“A,B and C are: “,a,b,c)
sum=a+b+c
#print(“Sum is”,sum)
return sum
out = mysum3(9,18,27)
print(“Out =”,out)
out = mysum3(9,18)
print(“Out =”,out)
# 0, 1,1,2,3,5… fibonacci numbers
def checkvalue(a,b):
global h
print(“H = “,h)
h = 99
print(“2 H = “,h)
if a>b:
return (“is”,a,“a”)
elif b>a:
return (“is”,b,“b”)
else:
return (“not”,)
h=100
result =checkvalue(10,20)
if result[0]==“not”:
print(“Both values are equal”)
else:
print(f”Variable {result[2]} with value {result[1]} is greater”)
# Session on MODULES
#Create a python file with name p2.py and paste below programs there
#Functions
# positional and required
# keyword
# default values
# variable length arguments
def mysum1(a,b):
return a+b
def mymultiple(a,b):
print(“a * b = “,a*b)
def my_sample_func(a,b,c):
print(“A,B,C = “,a,b,c)
def myfunc1(*nums,**details):
“””This is a sample function to demonstrate working of a variable length parameters
Input:
nums: will take all the values as tuple. it can be empty as well
details: store all keyword arguments like a dictionary
Return:
doesnt return anything”””
print(type(nums), type(details)) #tuple, dictionary
for i in nums:
print(i,end=“, “)
print()
for k,v in details.items():
print(k,v)
if __name__ == “__main__”:
myfunc1(23,21,14,12,15,26,name=“Sachin”,age=49,place=“Mumbai”)
myfunc1(name=“Sachin”,age=49,place=“Mumbai”)
#DocString – this is
print(print.__doc__)
print(“===”)
print(input.__doc__)
print(“===”)
print(myfunc1.__doc__)
# positional and required
# keyword
# default values
# variable length arguments
def mysum1(a,b):
return a+b
def mymultiple(a,b):
print(“a * b = “,a*b)
def my_sample_func(a,b,c):
print(“A,B,C = “,a,b,c)
def myfunc1(*nums,**details):
“””This is a sample function to demonstrate working of a variable length parameters
Input:
nums: will take all the values as tuple. it can be empty as well
details: store all keyword arguments like a dictionary
Return:
doesnt return anything”””
print(type(nums), type(details)) #tuple, dictionary
for i in nums:
print(i,end=“, “)
print()
for k,v in details.items():
print(k,v)
if __name__ == “__main__”:
myfunc1(23,21,14,12,15,26,name=“Sachin”,age=49,place=“Mumbai”)
myfunc1(name=“Sachin”,age=49,place=“Mumbai”)
#DocString – this is
print(print.__doc__)
print(“===”)
print(input.__doc__)
print(“===”)
print(myfunc1.__doc__)
#Run below programs from different file
#import p2 as Amazing
from p2 import mymultiple, my_sample_func
#decorators
def my_main():
”’ Example of a function inside a function”’
print(“First line in function”)
def my_subfunc():
print(“First line inside sub func”)
print(“Second line in main function”)
my_subfunc()
print(“Third line in main function”)
my_subfunc()
print(“4th line in main function”)
my_main()
def my_fun2():
print(“First line from my_fun2”)
def my_fun3():
print(“First line from my_fun3”)
def my_fun1(var):
print(“First line from my_fun1”)
var()
if __name__ ==“__main__”:
mymultiple(10,20)
my_sample_func(10,50,80)
#calling my_fun2 from my_fun1
my_fun1(my_fun2) #passing function name as parameter
#calling my_fun3 from my_fun1
my_fun1(my_fun3) # passing function name as parameter
from p2 import mymultiple, my_sample_func
#decorators
def my_main():
”’ Example of a function inside a function”’
print(“First line in function”)
def my_subfunc():
print(“First line inside sub func”)
print(“Second line in main function”)
my_subfunc()
print(“Third line in main function”)
my_subfunc()
print(“4th line in main function”)
my_main()
def my_fun2():
print(“First line from my_fun2”)
def my_fun3():
print(“First line from my_fun3”)
def my_fun1(var):
print(“First line from my_fun1”)
var()
if __name__ ==“__main__”:
mymultiple(10,20)
my_sample_func(10,50,80)
#calling my_fun2 from my_fun1
my_fun1(my_fun2) #passing function name as parameter
#calling my_fun3 from my_fun1
my_fun1(my_fun3) # passing function name as parameter
#Recursive functions – they call themselves
import time
def myfacto(n):
if n ==1:
return 1
return n * myfacto(n-1)
start1 = time.time()
out = myfacto(9)
end1 = time.time()
print(“Factorial of 10 is: “,out)
print(“Total time taken by recursion is:”,(end1-start1))
def myfacto2(n):
prod = 1
for i in range(1,n+1):
prod*=i
return prod
start2 = time.time()
out = myfacto2(9)
end2 = time.time()
print(“Factorial of 10 using Loops is: “,out)
print(“Total time taken by loop is:”,(end2-start2))
import random
var1 = random.randint(1,100)
print(“random number = “,var1)
print(“random number- between 0 and 1: “,random.random())
list1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
list2 = [“Apple”,“Banana”,“Cherry”,“Grapes”,“Guava”,“Mango”]
print(“Rolling the dice: “,random.choice(list2))
from datetime import date,datetime,time,timedelta,timezone, tzinfo
from pytz import timezone
#import datetime
print(“Current time = “,datetime.now())
print(“Yesterdat time = “,datetime.now()-timedelta(days=1))
print(“Today’s date: “,datetime.now().strftime(‘%Y-%m-%d’))
print(“This Month: “,datetime.now().month)
date_utc = datetime.now().replace(tzinfo=timezone(‘UTC’))
print(date_utc)
date_utc = datetime.now().replace(tzinfo=timezone(‘Asia/Kolkata’))
print(date_utc)
date_utc = datetime.now().replace(tzinfo=timezone(‘US/Eastern’))
print(date_utc)
import time
def myfacto(n):
if n ==1:
return 1
return n * myfacto(n-1)
start1 = time.time()
out = myfacto(9)
end1 = time.time()
print(“Factorial of 10 is: “,out)
print(“Total time taken by recursion is:”,(end1-start1))
def myfacto2(n):
prod = 1
for i in range(1,n+1):
prod*=i
return prod
start2 = time.time()
out = myfacto2(9)
end2 = time.time()
print(“Factorial of 10 using Loops is: “,out)
print(“Total time taken by loop is:”,(end2-start2))
import random
var1 = random.randint(1,100)
print(“random number = “,var1)
print(“random number- between 0 and 1: “,random.random())
list1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
list2 = [“Apple”,“Banana”,“Cherry”,“Grapes”,“Guava”,“Mango”]
print(“Rolling the dice: “,random.choice(list2))
from datetime import date,datetime,time,timedelta,timezone, tzinfo
from pytz import timezone
#import datetime
print(“Current time = “,datetime.now())
print(“Yesterdat time = “,datetime.now()-timedelta(days=1))
print(“Today’s date: “,datetime.now().strftime(‘%Y-%m-%d’))
print(“This Month: “,datetime.now().month)
date_utc = datetime.now().replace(tzinfo=timezone(‘UTC’))
print(date_utc)
date_utc = datetime.now().replace(tzinfo=timezone(‘Asia/Kolkata’))
print(date_utc)
date_utc = datetime.now().replace(tzinfo=timezone(‘US/Eastern’))
print(date_utc)
# properties we mean – methods (functions) and variables
# class and object levels
class Books:
num_of_books = 0 #class variable
def __init__(self,title=“”,author=“”): #object method
self.title=title #object variable
self.author=author
Books.num_of_books+=1
def display_book(self):
print(“Title of the book is”,self.title)
print(“Author of the book is”,self.author)
print(“Total books created is”,Books.num_of_books)
@classmethod
def display_classdetails(cls):
print(“Total number of books =”,cls.num_of_books)
b1=Books(“Python Programming”,“Swapnil Saurav”)
#b1.create_book()
b1.display_book()
b2=Books(“Machine Learning”,“Saurav”)
b3=Books(“Retail Management”,“Swapnil”)
b4=Books(“Data Visualization”,“Swapnil”)
#b2.create_book()
b2.display_book()
b1.display_book()
b3.display_classdetails()
b4.display_classdetails()
b1.display_classdetails()
Books.display_classdetails()
b3.display_book()
# add and subtract
class MyMasthsOps:
def __init__(self,a,b):
self.num1 = a
self.num2 = b
def addition(self):
return self.num1 + self.num2
def subtraction(self):
return self.num1 – self.num2
op1 = MyMasthsOps(10,5)
print(“Addition: “,op1.addition())
print(“Subtraction: “,op1.subtraction())
# class and object levels
class Books:
num_of_books = 0 #class variable
def __init__(self,title=“”,author=“”): #object method
self.title=title #object variable
self.author=author
Books.num_of_books+=1
def display_book(self):
print(“Title of the book is”,self.title)
print(“Author of the book is”,self.author)
print(“Total books created is”,Books.num_of_books)
@classmethod
def display_classdetails(cls):
print(“Total number of books =”,cls.num_of_books)
b1=Books(“Python Programming”,“Swapnil Saurav”)
#b1.create_book()
b1.display_book()
b2=Books(“Machine Learning”,“Saurav”)
b3=Books(“Retail Management”,“Swapnil”)
b4=Books(“Data Visualization”,“Swapnil”)
#b2.create_book()
b2.display_book()
b1.display_book()
b3.display_classdetails()
b4.display_classdetails()
b1.display_classdetails()
Books.display_classdetails()
b3.display_book()
# add and subtract
class MyMasthsOps:
def __init__(self,a,b):
self.num1 = a
self.num2 = b
def addition(self):
return self.num1 + self.num2
def subtraction(self):
return self.num1 – self.num2
op1 = MyMasthsOps(10,5)
print(“Addition: “,op1.addition())
print(“Subtraction: “,op1.subtraction())
#Class and Objects
class Cart:
items_in_store=[{“item_code”:“100”,“Item_Description”:“Blue color Shirt”,“Cost”:40},
{“item_code”:“101”,“Item_Description”:“Chips Packet”,“Cost”:2},
{“item_code”:“102”,“Item_Description”:“Chocolate Royal”,“Cost”:5},
{“item_code”:“103”,“Item_Description”:“Bread Big packet”,“Cost”:7},
{“item_code”:“104”,“Item_Description”:“Shoes 9C”,“Cost”:30},
{“item_code”:“105”,“Item_Description”:“Carry Bag 9in”,“Cost”:70},
{“item_code”:“106”,“Item_Description”:“Pen Blue Rey”,“Cost”:10}]
def __init__(self):
self.list_of_items=[]
def add_item(self):
available =“N”
temp_dict = {“item_code”:“”,“item_desc”:“”,“price”:0,“quantity”:0}
icode= input(“Enter the item code: “)
for item in Cart.items_in_store:
if icode ==item[‘item_code’]:
available = “Y”
temp_dict[‘item_code’] = item[‘item_code’]
temp_dict[‘item_desc’] = item[‘Item_Description’]
temp_dict[‘price’] = item[‘Cost’]
if available==“Y”:
quan = int(input(“Enter the quantity:”))
temp_dict[‘quantity’] = quan
self.list_of_items.append(temp_dict)
print(“Item has been added to your shopping cart!”)
else:
print(“This item is not available right now!”)
def display_items(self):
for item in self.list_of_items:
print(item)
def mainmenu(self):
print(“Main Menu:”)
print(“1. Add Item to the Cart”)
print(“2. Remove Item from the Cart”)
print(“3. Display the content of the cart”)
print(“4. Exit”)
choice=input(“Enter your choice: “)
return choice
if __name__ == ‘__main__’:
cart1 = Cart()
while True:
ch = cart1.mainmenu()
if ch==“1”:
cart1.add_item()
elif ch==“2”:
pass
elif ch==“3”:
cart1.display_items()
elif ch==“4”:
break
else:
print(“Invalid Option, try again!”)
class Cart:
items_in_store=[{“item_code”:“100”,“Item_Description”:“Blue color Shirt”,“Cost”:40},
{“item_code”:“101”,“Item_Description”:“Chips Packet”,“Cost”:2},
{“item_code”:“102”,“Item_Description”:“Chocolate Royal”,“Cost”:5},
{“item_code”:“103”,“Item_Description”:“Bread Big packet”,“Cost”:7},
{“item_code”:“104”,“Item_Description”:“Shoes 9C”,“Cost”:30},
{“item_code”:“105”,“Item_Description”:“Carry Bag 9in”,“Cost”:70},
{“item_code”:“106”,“Item_Description”:“Pen Blue Rey”,“Cost”:10}]
def __init__(self):
self.list_of_items=[]
def add_item(self):
available =“N”
temp_dict = {“item_code”:“”,“item_desc”:“”,“price”:0,“quantity”:0}
icode= input(“Enter the item code: “)
for item in Cart.items_in_store:
if icode ==item[‘item_code’]:
available = “Y”
temp_dict[‘item_code’] = item[‘item_code’]
temp_dict[‘item_desc’] = item[‘Item_Description’]
temp_dict[‘price’] = item[‘Cost’]
if available==“Y”:
quan = int(input(“Enter the quantity:”))
temp_dict[‘quantity’] = quan
self.list_of_items.append(temp_dict)
print(“Item has been added to your shopping cart!”)
else:
print(“This item is not available right now!”)
def display_items(self):
for item in self.list_of_items:
print(item)
def mainmenu(self):
print(“Main Menu:”)
print(“1. Add Item to the Cart”)
print(“2. Remove Item from the Cart”)
print(“3. Display the content of the cart”)
print(“4. Exit”)
choice=input(“Enter your choice: “)
return choice
if __name__ == ‘__main__’:
cart1 = Cart()
while True:
ch = cart1.mainmenu()
if ch==“1”:
cart1.add_item()
elif ch==“2”:
pass
elif ch==“3”:
cart1.display_items()
elif ch==“4”:
break
else:
print(“Invalid Option, try again!”)
# CRUD – Create new data, Read existing data, Update (edit the existing data) & Deleting existing data
# RDBMS – relational database management system
# database structure – logical (how we use the database) and physical (actual files that are saved)
# DBA, Database Developers & Database Architect
# DBA – installing and making sure that the databases are up and running
# OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) v OLAP (Online Analytical Processing)
## CRUD – C, U,D=80%, 20% R v 99% – reading
# Table: Students
# ROLLNO NAME GRADE EMAILID PHONE
# 1 Sachin 5 sa@sa.com 123
# 2 Laxman 7 lax@lax.com 231
# Table: Competitions
# COMPID NAME DOC ORG CONTACTNO
#Table: STUDENTCOMPETITIONS
# ID ROLLNO COMPID RANK
# RDBMS – relational database management system
# database structure – logical (how we use the database) and physical (actual files that are saved)
# DBA, Database Developers & Database Architect
# DBA – installing and making sure that the databases are up and running
# OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) v OLAP (Online Analytical Processing)
## CRUD – C, U,D=80%, 20% R v 99% – reading
# Table: Students
# ROLLNO NAME GRADE EMAILID PHONE
# 1 Sachin 5 sa@sa.com 123
# 2 Laxman 7 lax@lax.com 231
# Table: Competitions
# COMPID NAME DOC ORG CONTACTNO
#Table: STUDENTCOMPETITIONS
# ID ROLLNO COMPID RANK
class Library:
book_count = 0 #class level variable
# __init__() is automatically called when you create the object
def __init__(self,title,author,price): #object level method
self.title = title #object level variable
self.author = author #object level variable
self.price = price #object level variable
self.copies = –1
Library.book_count +=1 #Library.book_count = Library.book_count + 1
def print_info(self):
print(” Printing Book Info”)
print(“———————-“)
print(“Title = “,self.title)
print(“Author = “,self.author)
print(“Price = “,self.price)
def set_copies(self,copies=10):
self.copies = copies
def get_copies(self):
print(f”Total copies available for the book {self.title} is {self.copies}“)
return self.copies
b1 = Library(“Strangeness”,“George”, 13.50)
b2 = Library(“Python”,“Swapnil”, 19.50)
b3 = Library(“Machine Learning”,“Advait”, 33.50)
print(b1.book_count)
print(b2.book_count)
print(b3.book_count)
print(Library.book_count)
print(b1.title)
print(b2.title)
print(b3.title)
b3.print_info()
b2.set_copies(7)
b2.get_copies()
if b1.get_copies() <0:
b1.set_copies(5)
b1.get_copies()
book_count = 0 #class level variable
# __init__() is automatically called when you create the object
def __init__(self,title,author,price): #object level method
self.title = title #object level variable
self.author = author #object level variable
self.price = price #object level variable
self.copies = –1
Library.book_count +=1 #Library.book_count = Library.book_count + 1
def print_info(self):
print(” Printing Book Info”)
print(“———————-“)
print(“Title = “,self.title)
print(“Author = “,self.author)
print(“Price = “,self.price)
def set_copies(self,copies=10):
self.copies = copies
def get_copies(self):
print(f”Total copies available for the book {self.title} is {self.copies}“)
return self.copies
b1 = Library(“Strangeness”,“George”, 13.50)
b2 = Library(“Python”,“Swapnil”, 19.50)
b3 = Library(“Machine Learning”,“Advait”, 33.50)
print(b1.book_count)
print(b2.book_count)
print(b3.book_count)
print(Library.book_count)
print(b1.title)
print(b2.title)
print(b3.title)
b3.print_info()
b2.set_copies(7)
b2.get_copies()
if b1.get_copies() <0:
b1.set_copies(5)
b1.get_copies()
Class Calculation
1. use init to assign two variables
2. def add(self) , def sub(self), def mul(self), def div(self)
##Main Program
input a and b
c1 = Calculation(a,b)
create: def menu()
1. use init to assign two variables
2. def add(self) , def sub(self), def mul(self), def div(self)
##Main Program
input a and b
c1 = Calculation(a,b)
create: def menu()
# Exceptions
# example 1: ValueError – when u convert non number to integer
”’
1. Syntax error:
print(“Hello) #SyntaxError: unterminated string literal (detected at line 7)
2. Logical Error: Sum of two numbers
a,b = 4,5
print(a*b)
3. Exceptions: Runtime error
1. int(‘n’) # ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: ‘num’
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
”’
#WAP to input two numbers and perform their division
try: #try block is used to check the exception
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
except ValueError: #if there is ValueError, code comes here
print(“You have given an invalid number, resetting it to zero”)
num = 0
except Exception: # if previous exception not valid then it comes here
print(“Sum error has occurred. Exiting the program”)
exit(0)
else: # if there is no error, then comes to else (not mandatory)
print(“You are doing good. No error so far!”)
finally: # error or no error, this is called. again its not mandatory
print(“You are doing good.”)
try:
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
except ValueError: #if there is ValueError, code comes here
print(“You have given an invalid number, resetting it to one”)
dem = 1
try:
div = num/dem
except ZeroDivisionError:
print(“Denominator cant be zero!!! We are terminating the program”)
else:
print(“Division of given values is”,div)
# example 1: ValueError – when u convert non number to integer
”’
1. Syntax error:
print(“Hello) #SyntaxError: unterminated string literal (detected at line 7)
2. Logical Error: Sum of two numbers
a,b = 4,5
print(a*b)
3. Exceptions: Runtime error
1. int(‘n’) # ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: ‘num’
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
”’
#WAP to input two numbers and perform their division
try: #try block is used to check the exception
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
except ValueError: #if there is ValueError, code comes here
print(“You have given an invalid number, resetting it to zero”)
num = 0
except Exception: # if previous exception not valid then it comes here
print(“Sum error has occurred. Exiting the program”)
exit(0)
else: # if there is no error, then comes to else (not mandatory)
print(“You are doing good. No error so far!”)
finally: # error or no error, this is called. again its not mandatory
print(“You are doing good.”)
try:
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
except ValueError: #if there is ValueError, code comes here
print(“You have given an invalid number, resetting it to one”)
dem = 1
try:
div = num/dem
except ZeroDivisionError:
print(“Denominator cant be zero!!! We are terminating the program”)
else:
print(“Division of given values is”,div)
# WAP to input and divide two numbers
try:
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
divide = num/dem
except ValueError:
print(“Sorry, we cant move ahead because of the invalid number”)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print(“Sorry, we cant move ahead because we cant handle zero as denominator”)
else:
print(“Answer is”,divide)
finally:
print(“thank you for using our calculator. See you soon…”)
try:
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
divide = num/dem
except ValueError:
print(“Sorry, we cant move ahead because of the invalid number”)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print(“Sorry, we cant move ahead because we cant handle zero as denominator”)
else:
print(“Answer is”,divide)
finally:
print(“thank you for using our calculator. See you soon…”)
# WAP to input and divide two numbers
try:
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
divide = num / dem
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
except Exception:
print(“Some error has occurred. We need to stop”)
else:
print(“Answer is”,divide)
finally:
print(“thank you for using our calculator. See you soon…”)
## Another approach
# WAP to input and divide two numbers
while True:
try:
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
else:
break
while True:
try:
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
else:
if dem ==0:
print(“Denominator cant be zero, enter again!”)
else:
break
divide = num/dem
print(“Answer is”,divide)
## Another approach using our own class
# WAP to input and divide two numbers
#creating by own exception
class ZeroValueError(Exception):
def __init__(self,value):
self.val = value
while True:
try:
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
else:
break
while True:
try:
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
if dem ==0:
raise ZeroValueError(dem)
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
except ZeroValueError as zde:
print(f”Denominator cant be {zde.val}, enter again!”)
else:
break
divide = num/dem
print(“Answer is”,divide)
#Another approach using Assert method
# WAP to input and divide two numbers
while True:
try:
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
else:
break
while True:
try:
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
if dem ==0:
assert (dem!=0),“Denominator cant be zero, lets stop!”
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
except AssertionError:
print(“Dont give zero for denominator”)
else:
break
divide = num/dem
print(“Answer is”,divide)
try:
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
divide = num / dem
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
except Exception:
print(“Some error has occurred. We need to stop”)
else:
print(“Answer is”,divide)
finally:
print(“thank you for using our calculator. See you soon…”)
## Another approach
# WAP to input and divide two numbers
while True:
try:
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
else:
break
while True:
try:
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
else:
if dem ==0:
print(“Denominator cant be zero, enter again!”)
else:
break
divide = num/dem
print(“Answer is”,divide)
## Another approach using our own class
# WAP to input and divide two numbers
#creating by own exception
class ZeroValueError(Exception):
def __init__(self,value):
self.val = value
while True:
try:
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
else:
break
while True:
try:
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
if dem ==0:
raise ZeroValueError(dem)
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
except ZeroValueError as zde:
print(f”Denominator cant be {zde.val}, enter again!”)
else:
break
divide = num/dem
print(“Answer is”,divide)
#Another approach using Assert method
# WAP to input and divide two numbers
while True:
try:
num = int(input(“Enter the numerator: “))
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
else:
break
while True:
try:
dem = int(input(“Enter the denominator: “))
if dem ==0:
assert (dem!=0),“Denominator cant be zero, lets stop!”
except ValueError:
print(“Invalid number”)
except AssertionError:
print(“Dont give zero for denominator”)
else:
break
divide = num/dem
print(“Answer is”,divide)
# Files – txt, csv
# r (read mode): only reading, file must be there
# w (write mode): only writing, file needn’t be there (it will be created), previous content gets deleted
# a (append mode): only writing, added on the previous content
# relative path: will not have drive name, can start with / or \\
# absolute path: will start with drive name
filename = “MyPoem.txt”
filename2 = “c:/myfolder/Myfile.txt”
# if file isnt there for read mode:
# FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘/MyPack1/MyPoem.txt’
fileobj = open(filename,“w”)
fileobj.close()
# r (read mode): only reading, file must be there
# w (write mode): only writing, file needn’t be there (it will be created), previous content gets deleted
# a (append mode): only writing, added on the previous content
# relative path: will not have drive name, can start with / or \\
# absolute path: will start with drive name
filename = “MyPoem.txt”
filename2 = “c:/myfolder/Myfile.txt”
# if file isnt there for read mode:
# FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘/MyPack1/MyPoem.txt’
fileobj = open(filename,“w”)
fileobj.close()
”’
Reading & Writing txt files. Modes in which you can open a txt files:
1. r – reading (you cant write to it)
2. w – writing (this will delete previous content and add the new content only)
3. a – append (old data will be ratained and new data is added below)
4. r+ – reading and writing
5. w+ – writing and reading
6. a+ – writing and reading
operations:
reading: read(), readline(), readlines()
writing: write(), writelines()
1. Open the file using a handle to the object
2. whatever you want to do – read/write/
3. Close the file
Absolute path: complete path, with the drive letter: D:\\Files\\file.txt
Relative path: path is mentioned with respect to the python file which has the code: /data/abc.txt
”’
file=“MyLearn.txt”
try:
fileobj = open(file,“r”)
except FileNotFoundError:
fileobj1 = open(file, “w”)
fileobj1.close()
fileobj = open(file, “r”)
content = fileobj.read(10)
print(content)
#seek() – instruction to go to a perticular position
#fileobj.seek(1) #goes to the beginning of the content
content1 = fileobj.readline()
print(“Content after readline:\n“,content1)
# read whats for H?
fileobj.seek(0)
content2 = fileobj.readlines()
print(content2)
character = “B”
for sentence in content2:
if sentence[0]==character:
print(sentence)
fileobj.close()
fileobj = open(file,“a”)
inp_content=”’
L: Lion
M: Monkey
N: Needle
O: Opal
P: Peach
”’
fileobj.write(inp_content)
inp_content2 = [‘Q: Queen\n‘,‘R: Rain\n‘,‘S: Ship\n‘,‘T: Teapot’]
fileobj.writelines(inp_content2)
fileobj.close()
### Writing usage
file=“MyLearn.txt”
fileobj = open(file,“a”)
inp_content=”’
L: Lion
M: Monkey
N: Needle
O: Opal
P: Peach
”’
fileobj.write(inp_content)
inp_content2 = [‘Q: Queen\n‘,‘R: Rain\n‘,‘S: Ship\n‘,‘T: Teapot’]
fileobj.writelines(inp_content2)
fileobj.close()
Reading & Writing txt files. Modes in which you can open a txt files:
1. r – reading (you cant write to it)
2. w – writing (this will delete previous content and add the new content only)
3. a – append (old data will be ratained and new data is added below)
4. r+ – reading and writing
5. w+ – writing and reading
6. a+ – writing and reading
operations:
reading: read(), readline(), readlines()
writing: write(), writelines()
1. Open the file using a handle to the object
2. whatever you want to do – read/write/
3. Close the file
Absolute path: complete path, with the drive letter: D:\\Files\\file.txt
Relative path: path is mentioned with respect to the python file which has the code: /data/abc.txt
”’
file=“MyLearn.txt”
try:
fileobj = open(file,“r”)
except FileNotFoundError:
fileobj1 = open(file, “w”)
fileobj1.close()
fileobj = open(file, “r”)
content = fileobj.read(10)
print(content)
#seek() – instruction to go to a perticular position
#fileobj.seek(1) #goes to the beginning of the content
content1 = fileobj.readline()
print(“Content after readline:\n“,content1)
# read whats for H?
fileobj.seek(0)
content2 = fileobj.readlines()
print(content2)
character = “B”
for sentence in content2:
if sentence[0]==character:
print(sentence)
fileobj.close()
fileobj = open(file,“a”)
inp_content=”’
L: Lion
M: Monkey
N: Needle
O: Opal
P: Peach
”’
fileobj.write(inp_content)
inp_content2 = [‘Q: Queen\n‘,‘R: Rain\n‘,‘S: Ship\n‘,‘T: Teapot’]
fileobj.writelines(inp_content2)
fileobj.close()
### Writing usage
file=“MyLearn.txt”
fileobj = open(file,“a”)
inp_content=”’
L: Lion
M: Monkey
N: Needle
O: Opal
P: Peach
”’
fileobj.write(inp_content)
inp_content2 = [‘Q: Queen\n‘,‘R: Rain\n‘,‘S: Ship\n‘,‘T: Teapot’]
fileobj.writelines(inp_content2)
fileobj.close()
”’
1. Read from the diary
2. Write to the diary
2.
11-JUNE-2023: Today we had singing practice at school
1.
Which date: 11-JUNE-2023
Output: Today we had singing practice at school
”’
1. Read from the diary
2. Write to the diary
2.
11-JUNE-2023: Today we had singing practice at school
1.
Which date: 11-JUNE-2023
Output: Today we had singing practice at school
”’
import csv
file = “MyData.csv”
fileobj = open(file, mode=“a”, newline=“”)
csvwriter = csv.writer(fileobj, delimiter=“,”,quotechar=‘”‘,quoting=csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL)
while True:
content = []
name=input(“Enter your name:”)
content.append(name)
city=input(“Enter your city: “)
content.append(city)
score=input(“Enter your score:”)
content.append(score)
csvwriter.writerow(content)
ch=input(“Enter any value to continue adding:”)
if len(ch)==0:
break
fileobj.close()
”’ Reading the data from the CSV file”’
fileobj = open(file) # default mode is reading (r)
csvreader = csv.reader(fileobj,delimiter=“,”)
total = 0
for each_row in csvreader:
total+=int(each_row[2])
print(“Total = “,total)
file = “MyData.csv”
fileobj = open(file, mode=“a”, newline=“”)
csvwriter = csv.writer(fileobj, delimiter=“,”,quotechar=‘”‘,quoting=csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL)
while True:
content = []
name=input(“Enter your name:”)
content.append(name)
city=input(“Enter your city: “)
content.append(city)
score=input(“Enter your score:”)
content.append(score)
csvwriter.writerow(content)
ch=input(“Enter any value to continue adding:”)
if len(ch)==0:
break
fileobj.close()
”’ Reading the data from the CSV file”’
fileobj = open(file) # default mode is reading (r)
csvreader = csv.reader(fileobj,delimiter=“,”)
total = 0
for each_row in csvreader:
total+=int(each_row[2])
print(“Total = “,total)
#CSV files reader / writer
# name
# lastname, firstname
import csv
filename = “FruitProduction.csv”
fileobj = open(filename,“w”,newline=“”)
writerobj = csv.writer(fileobj, delimiter=“,”,quotechar=‘”‘,quoting=csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL)
first_row = [‘Year’,‘Apple’,‘Banana’,‘Mango’,‘Oranges’]
second_row = [‘2023’,65,34,29,56]
third_row = [‘2022’,45,29,23,45]
forth_row = [‘2021’,39,29,19,25]
writerobj.writerow(first_row)
writerobj.writerow(second_row)
writerobj.writerow(third_row)
writerobj.writerow(forth_row)
fileobj.close()
fileobj = open(filename) #default read mode
readerobj = csv.reader(fileobj,delimiter=‘,’)
for row in readerobj:
print(row)
fileobj.close()
fileobj = open(filename)
#1. Show to Apple production for last 3 years
readerobj = csv.reader(fileobj,delimiter=‘,’)
print(“Apple production were:”)
for row in readerobj:
print(row[0],“:”,row[1])
fileobj.close()
#Highest production of Mango
fileobj = open(filename)
#2. Highest Mango production
readerobj = csv.reader(fileobj,delimiter=‘,’)
mango_high,year_high = –1,-1
linecount=0
for row in readerobj:
if linecount==0:
linecount+=1
else:
if int(row[3]) > mango_high:
mango_high=int(row[3])
year_high = row[0]
print(“Highest Mango production was”,mango_high,“in the year”,year_high)
fileobj.close()
# name
# lastname, firstname
import csv
filename = “FruitProduction.csv”
fileobj = open(filename,“w”,newline=“”)
writerobj = csv.writer(fileobj, delimiter=“,”,quotechar=‘”‘,quoting=csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL)
first_row = [‘Year’,‘Apple’,‘Banana’,‘Mango’,‘Oranges’]
second_row = [‘2023’,65,34,29,56]
third_row = [‘2022’,45,29,23,45]
forth_row = [‘2021’,39,29,19,25]
writerobj.writerow(first_row)
writerobj.writerow(second_row)
writerobj.writerow(third_row)
writerobj.writerow(forth_row)
fileobj.close()
fileobj = open(filename) #default read mode
readerobj = csv.reader(fileobj,delimiter=‘,’)
for row in readerobj:
print(row)
fileobj.close()
fileobj = open(filename)
#1. Show to Apple production for last 3 years
readerobj = csv.reader(fileobj,delimiter=‘,’)
print(“Apple production were:”)
for row in readerobj:
print(row[0],“:”,row[1])
fileobj.close()
#Highest production of Mango
fileobj = open(filename)
#2. Highest Mango production
readerobj = csv.reader(fileobj,delimiter=‘,’)
mango_high,year_high = –1,-1
linecount=0
for row in readerobj:
if linecount==0:
linecount+=1
else:
if int(row[3]) > mango_high:
mango_high=int(row[3])
year_high = row[0]
print(“Highest Mango production was”,mango_high,“in the year”,year_high)
fileobj.close()
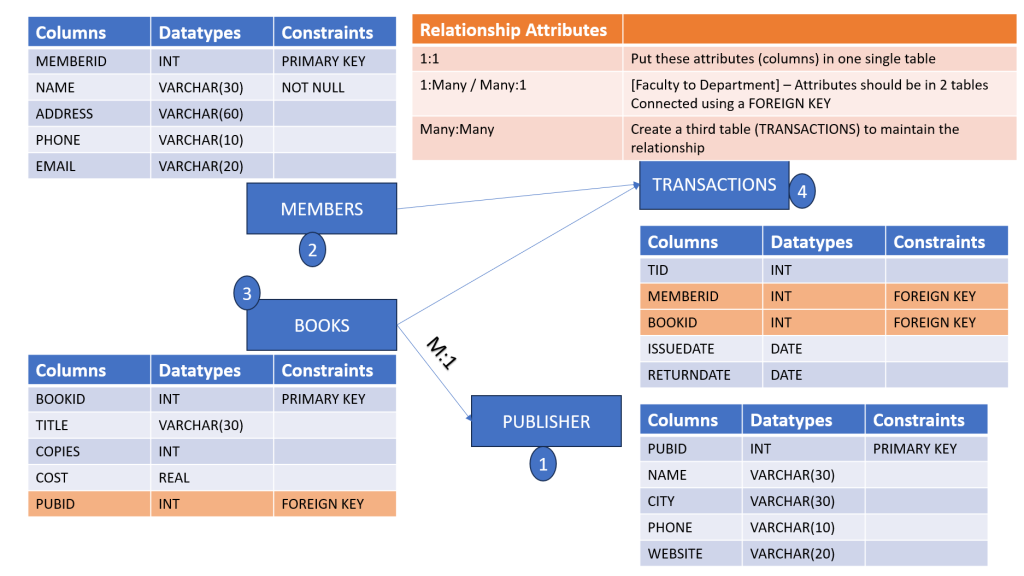
# pymysql library connects to MYSQL
# Books
# Publishers
import sqlite3
connection = sqlite3.Connection(‘BOOKSDB.SQLITE’)
cursorobj = connection.cursor()
# SQL – Structured Query Language
# Dropping an already existing table:
#cursorobj.execute(“DROP TABLE Publishers”)
#create a new table:
table1 = ”’
Create Table Publishers(
PUBID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
PUBNAME VARCHAR,
PUBCITY VARCHAR
)
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table1) #creates the table
#create a new table:
table2 = ”’
Create Table BOOKS(
BID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
TITLE VARCHAR,
AUTHOR VARCHAR,
PUBID INTEGER,
CONSTRAINT fk_pidid_cons Foreign Key (PUBID) References Publishers(PUBID)
)
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table2) #creates the table
# INSERT Commands are used to add data to the tables
insert_data = [‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubName, PubCity) values (101, “ABC International”,”New York”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers values (102,”Indigo Publishers”,”New Delhi”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubCity, PubName) values (105,”Hyderabad”,”Glocal Publishers”)’]
insert_data = [‘Insert into Books values (101,”Python Programming”,”Sachin”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (102,”Data Science Learning”,”Rohit”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (103,”SQL Programming”,”Virat”,105)’]
for statement in insert_data:
cursorobj.execute(statement)
connection.commit()
# Books
# Publishers
import sqlite3
connection = sqlite3.Connection(‘BOOKSDB.SQLITE’)
cursorobj = connection.cursor()
# SQL – Structured Query Language
# Dropping an already existing table:
#cursorobj.execute(“DROP TABLE Publishers”)
#create a new table:
table1 = ”’
Create Table Publishers(
PUBID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
PUBNAME VARCHAR,
PUBCITY VARCHAR
)
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table1) #creates the table
#create a new table:
table2 = ”’
Create Table BOOKS(
BID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
TITLE VARCHAR,
AUTHOR VARCHAR,
PUBID INTEGER,
CONSTRAINT fk_pidid_cons Foreign Key (PUBID) References Publishers(PUBID)
)
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table2) #creates the table
# INSERT Commands are used to add data to the tables
insert_data = [‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubName, PubCity) values (101, “ABC International”,”New York”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers values (102,”Indigo Publishers”,”New Delhi”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubCity, PubName) values (105,”Hyderabad”,”Glocal Publishers”)’]
insert_data = [‘Insert into Books values (101,”Python Programming”,”Sachin”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (102,”Data Science Learning”,”Rohit”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (103,”SQL Programming”,”Virat”,105)’]
for statement in insert_data:
cursorobj.execute(statement)
connection.commit()
# pymysql library connects to MYSQL
# Books
# Publishers
import sqlite3
connection = sqlite3.Connection(‘BOOKSDB.SQLITE’)
cursorobj = connection.cursor()
# SQL – Structured Query Language
# Dropping an already existing table:
#cursorobj.execute(“DROP TABLE Publishers”)
#create a new table:
table1 = ”’
Create Table Publishers(
PUBID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
PUBNAME VARCHAR,
PUBCITY VARCHAR
)
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table1) #creates the table
#create a new table:
table2 = ”’
Create Table BOOKS(
BID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
TITLE VARCHAR,
AUTHOR VARCHAR,
PUBID INTEGER,
CONSTRAINT fk_pidid_cons Foreign Key (PUBID) References Publishers(PUBID)
)
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table2) #creates the table
# INSERT Commands are used to add data to the tables
insert_data = [‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubName, PubCity) values (101, “ABC International”,”New York”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers values (102,”Indigo Publishers”,”New Delhi”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubCity, PubName) values (105,”Hyderabad”,”Glocal Publishers”)’]
insert_data = [‘Insert into Books values (101,”Python Programming”,”Sachin”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (102,”Data Science Learning”,”Rohit”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (103,”SQL Programming”,”Virat”,105)’]
”’
for statement in insert_data:
cursorobj.execute(statement)
connection.commit()
”’
# Read data from the database
q1 = “Select * from Publishers”
cursorobj.execute(q1)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
print(row)
q1 = “Select * from Books”
cursorobj.execute(q1)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
print(row)
#UPDATE
q3 =“Update Books Set Author =’Dhoni’ where BID=102 “
cursorobj.execute(q3)
connection.commit()
#DELETE
q3 =“Delete from Publishers where PUBID=101 “
cursorobj.execute(q3)
connection.commit()
q2 = “Select TITLE, PUBNAME, Author from Books t1, Publishers t2 where t1.PUBID=t2.PUBID”
cursorobj.execute(q2)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
#print(row)
print(f”{row[0]} which is written by {row[2]} is published by {row[1]}“)
# Books
# Publishers
import sqlite3
connection = sqlite3.Connection(‘BOOKSDB.SQLITE’)
cursorobj = connection.cursor()
# SQL – Structured Query Language
# Dropping an already existing table:
#cursorobj.execute(“DROP TABLE Publishers”)
#create a new table:
table1 = ”’
Create Table Publishers(
PUBID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
PUBNAME VARCHAR,
PUBCITY VARCHAR
)
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table1) #creates the table
#create a new table:
table2 = ”’
Create Table BOOKS(
BID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
TITLE VARCHAR,
AUTHOR VARCHAR,
PUBID INTEGER,
CONSTRAINT fk_pidid_cons Foreign Key (PUBID) References Publishers(PUBID)
)
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table2) #creates the table
# INSERT Commands are used to add data to the tables
insert_data = [‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubName, PubCity) values (101, “ABC International”,”New York”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers values (102,”Indigo Publishers”,”New Delhi”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubCity, PubName) values (105,”Hyderabad”,”Glocal Publishers”)’]
insert_data = [‘Insert into Books values (101,”Python Programming”,”Sachin”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (102,”Data Science Learning”,”Rohit”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (103,”SQL Programming”,”Virat”,105)’]
”’
for statement in insert_data:
cursorobj.execute(statement)
connection.commit()
”’
# Read data from the database
q1 = “Select * from Publishers”
cursorobj.execute(q1)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
print(row)
q1 = “Select * from Books”
cursorobj.execute(q1)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
print(row)
#UPDATE
q3 =“Update Books Set Author =’Dhoni’ where BID=102 “
cursorobj.execute(q3)
connection.commit()
#DELETE
q3 =“Delete from Publishers where PUBID=101 “
cursorobj.execute(q3)
connection.commit()
q2 = “Select TITLE, PUBNAME, Author from Books t1, Publishers t2 where t1.PUBID=t2.PUBID”
cursorobj.execute(q2)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
#print(row)
print(f”{row[0]} which is written by {row[2]} is published by {row[1]}“)
”’
Install MYSQL from
https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/
Installation steps:
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql-installation-excerpt/5.7/en/
or check this:
https://www.sqlshack.com/how-to-install-mysql-database-server-8-0-19-on-windows-10/
Components that we need:
1. Server – dont forget the admin (root) password
2. Client – server host, database, database username and password
3. Database
4. Workbench – UI tool to connect to the Server
”’
import pymysql
connection = pymysql.Connection(host=“localhost”,database=“advaitdb”,user=“root”,password=“learnSQL”)
cursorobj = connection.cursor()
# SQL – Structured Query Language
# Dropping an already existing table:
#cursorobj.execute(“DROP TABLE Publishers”)
#create a new table:
table1 = ”’
Create Table advaitdb.Publishers(
PUBID INT PRIMARY KEY,
PUBNAME VARCHAR(15),
PUBCITY VARCHAR(15)
);
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table1) #creates the table
#create a new table:
table2 = ”’
Create Table advaitdb.BOOKS(
BID INT PRIMARY KEY,
TITLE VARCHAR(15),
AUTHOR VARCHAR(15),
PUBID INT,
CONSTRAINT fk_pidid_cons Foreign Key (PUBID) References Publishers(PUBID)
)
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table2) #creates the table
# Alter is used to change the datatype
# Modify to change the current structure
alter_q =“ALTER TABLE publishers Modify Column PUBNAME varchar(40)”
#cursorobj.execute(alter_q)
alter_q =“ALTER TABLE Books Modify Column TITLE varchar(40)”
cursorobj.execute(alter_q)
# INSERT Commands are used to add data to the tables
insert_data = [‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubName, PubCity) values (101, “ABC International”,”New York”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers values (102,”Indigo Publishers”,”New Delhi”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubCity, PubName) values (105,”Hyderabad”,”Glocal Publishers”)’]
”’
for statement in insert_data:
cursorobj.execute(statement)
connection.commit()
”’
insert_data = [‘Insert into Books values (101,”Python Programming”,”Sachin”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (102,”Data Science Learning”,”Rohit”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (103,”SQL Programming”,”Virat”,105)’]
for statement in insert_data:
cursorobj.execute(statement)
connection.commit()
# Read data from the database
q1 = “Select * from Publishers”
cursorobj.execute(q1)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
print(row)
q1 = “Select * from Books”
cursorobj.execute(q1)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
print(row)
#UPDATE
q3 =“Update Books Set Author =’Dhoni’ where BID=102 “
cursorobj.execute(q3)
connection.commit()
#DELETE
q3 =“Delete from Publishers where PUBID=101 “
cursorobj.execute(q3)
connection.commit()
q2 = “Select TITLE, PUBNAME, Author from Books t1, Publishers t2 where t1.PUBID=t2.PUBID”
cursorobj.execute(q2)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
#print(row)
print(f”{row[0]} which is written by {row[2]} is published by {row[1]}“)
Install MYSQL from
https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/
Installation steps:
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql-installation-excerpt/5.7/en/
or check this:
https://www.sqlshack.com/how-to-install-mysql-database-server-8-0-19-on-windows-10/
Components that we need:
1. Server – dont forget the admin (root) password
2. Client – server host, database, database username and password
3. Database
4. Workbench – UI tool to connect to the Server
”’
import pymysql
connection = pymysql.Connection(host=“localhost”,database=“advaitdb”,user=“root”,password=“learnSQL”)
cursorobj = connection.cursor()
# SQL – Structured Query Language
# Dropping an already existing table:
#cursorobj.execute(“DROP TABLE Publishers”)
#create a new table:
table1 = ”’
Create Table advaitdb.Publishers(
PUBID INT PRIMARY KEY,
PUBNAME VARCHAR(15),
PUBCITY VARCHAR(15)
);
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table1) #creates the table
#create a new table:
table2 = ”’
Create Table advaitdb.BOOKS(
BID INT PRIMARY KEY,
TITLE VARCHAR(15),
AUTHOR VARCHAR(15),
PUBID INT,
CONSTRAINT fk_pidid_cons Foreign Key (PUBID) References Publishers(PUBID)
)
”’
#cursorobj.execute(table2) #creates the table
# Alter is used to change the datatype
# Modify to change the current structure
alter_q =“ALTER TABLE publishers Modify Column PUBNAME varchar(40)”
#cursorobj.execute(alter_q)
alter_q =“ALTER TABLE Books Modify Column TITLE varchar(40)”
cursorobj.execute(alter_q)
# INSERT Commands are used to add data to the tables
insert_data = [‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubName, PubCity) values (101, “ABC International”,”New York”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers values (102,”Indigo Publishers”,”New Delhi”)’,
‘Insert into Publishers (PubID, PubCity, PubName) values (105,”Hyderabad”,”Glocal Publishers”)’]
”’
for statement in insert_data:
cursorobj.execute(statement)
connection.commit()
”’
insert_data = [‘Insert into Books values (101,”Python Programming”,”Sachin”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (102,”Data Science Learning”,”Rohit”,102)’,
‘Insert into Books values (103,”SQL Programming”,”Virat”,105)’]
for statement in insert_data:
cursorobj.execute(statement)
connection.commit()
# Read data from the database
q1 = “Select * from Publishers”
cursorobj.execute(q1)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
print(row)
q1 = “Select * from Books”
cursorobj.execute(q1)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
print(row)
#UPDATE
q3 =“Update Books Set Author =’Dhoni’ where BID=102 “
cursorobj.execute(q3)
connection.commit()
#DELETE
q3 =“Delete from Publishers where PUBID=101 “
cursorobj.execute(q3)
connection.commit()
q2 = “Select TITLE, PUBNAME, Author from Books t1, Publishers t2 where t1.PUBID=t2.PUBID”
cursorobj.execute(q2)
results = cursorobj.fetchall()
print(type(results)) #<class ‘list’>
for row in results:
#print(row)
print(f”{row[0]} which is written by {row[2]} is published by {row[1]}“)


var1 = 5 #let’s take a variable called var1 and make it equal to 5
# number without decimal point – integer
#var1 is a variable of type integer
print(“var1”)
print(var1)
print(type(var1))
var1 = 5.0 #float – -inf to +inf with decimal point
print(type(var1))
var1 = 5j #complex (imaginary) – i
# square root of -25 = sq rt(25* -1) = 5j
print(type(var1))
print(5j * 5j)
# string – text (str)
var1 = “hello”
print(type(var1))
#5th basic data types – bool (boolean – 2 values: True / False)
var1 = True
print(type(var1))
#Functions for explicit conversion – convert data from given type to this:
# int(), float(), complex(), str(), bool()
var1 = int(“5”)
print(type(var1))
quantity =49
cost_pc = 51.89
total_cost = quantity * cost_pc
print(“Total quantity bought is”,quantity,”each one at a cost of”,cost_pc,”so the total cost is”,total_cost)
print(f”Total quantity bought is {quantity} each one at a cost of {cost_pc:.1f} so the total cost is {total_cost}”)
pl=”Rohit”
cn=”India”
pos=”captain”
print(f”Player {pl:<12} plays for {cn:^12} and is {pos:>20} of the team!”)
pl=”Mabwange”
cn=”Zimbabwe”
pos=”Wicket-keeper”
print(f”Player {pl:<12} plays for {cn:^12} and is {pos:>20} of the team!”)
num1 = int(input(“Enter first number to be added: “)) #default input will read as str
print(type(num1))
num2 = int(input(“Enter second number to be added: “))
print(type(num2))
print(num1+num2)