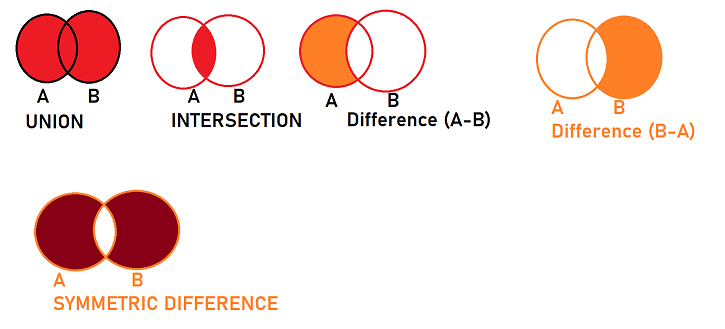
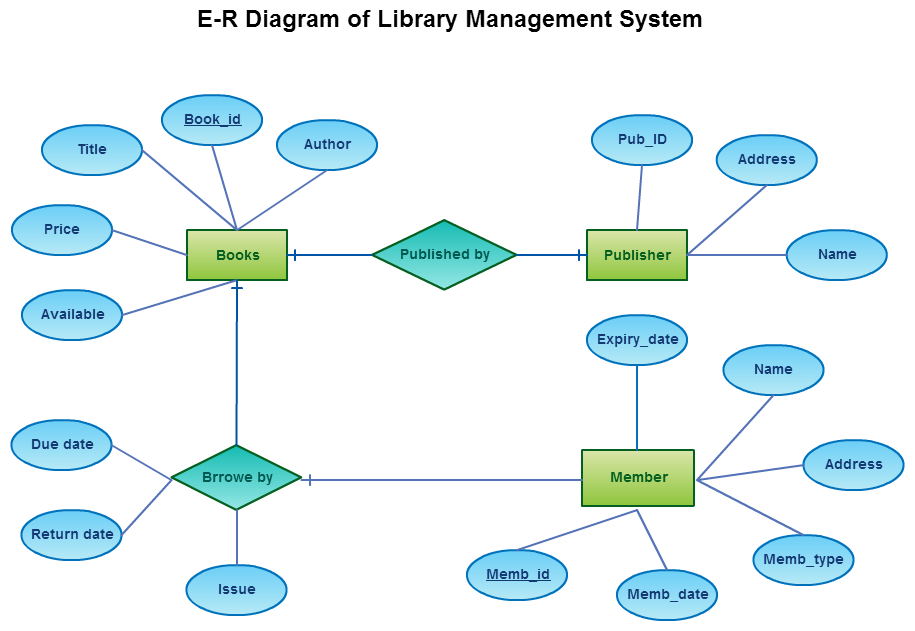
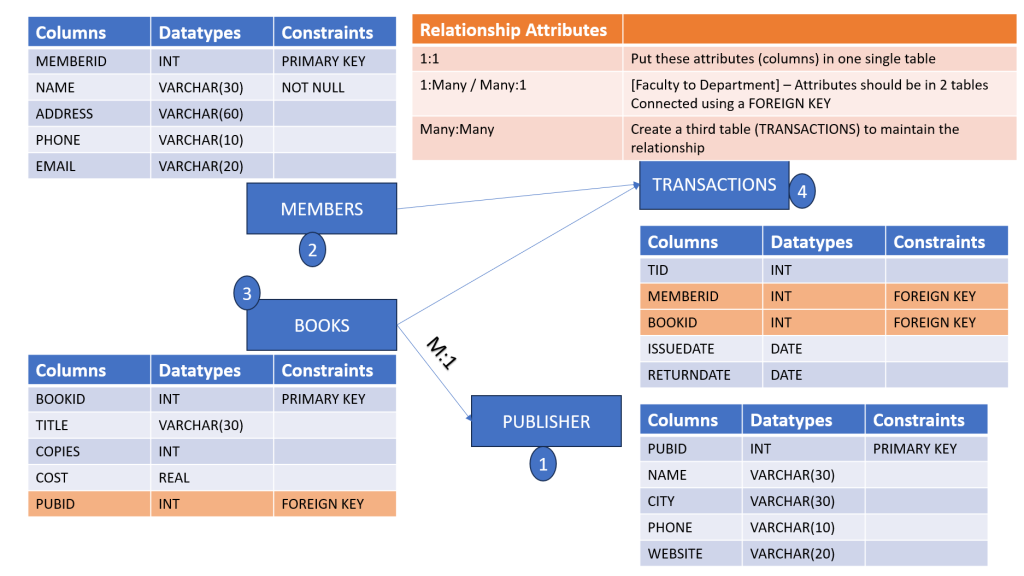
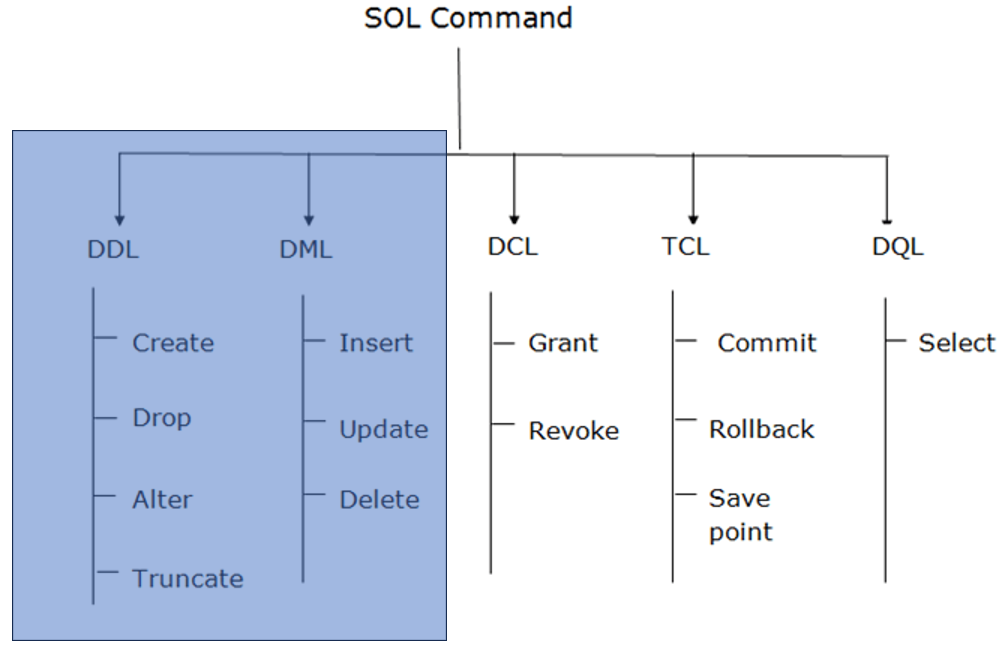
Python and Machine Learning Course May 2023
print(‘5 + 3 =’, 5+3)
pi = 3.1 # variable
g = 9.8
radius = 15
# area of a circle = pi * r square
# commentsm jhjkhjkhkjhjghg
print(“Area of a circle =”,3.1 * radius * radius)
# Write a program to find area and perimeter of a rectangle by taking length and breadth as input
length = 21
breadth = 38
area = length * breadth
perim = 2 * (length + breadth)
print(“Area of rectangle =”,area)
print(“Perimeter of rectangle =”,perim)
#Write a program to find area and perimeter of a square
side = 35
area = side * side
perim = 4 * side
print(“Area of square =”,area)
print(“Perimeter of square =”,perim)
#Find total and average of five numbers
num1 = 78
num2 = 82
num3 = 79
num4 = 91
num5 = 59
total = num1 + num2 + num3 + num4 + num5
avg = total / 5
print(“Total = “,total,”Average is”,avg)
num1, num2, num3,num4,num5 = 78,82,79,91,59
total = num1 + num2 + num3 + num4 + num5
avg = total / 5
print(“Total = “,total,“Average is”,avg)
x = 8
y = 2 * x * x – (10 * x) + 30 # expression
print(“Value of y =”,y)
#different types
# basic data types – they can store only one value at a time
# integer (int) – numbers without decimal values
num1 = 5
num2 = 0
num3 = –99 #<class ‘int’>
print(“1. “,type(num1)) #type(num1) – this is first to be called and then print() is called
# float (float) – decimal values
num1 = 5.0
num2 = 0.9
num3 = –99.1 #<class ‘float’>
print(“2. “,type(num1))
# string (str)
var1 = “Hello”
var2 = ‘Good Evening’
var3 = ”’Hi there”’
var4 = “””Python learning”””
print(type(var1), type(var2),type(var3),type(var4))
# boolean (bool) – True & False
var1 = True
var2 = False
print(type(var1), type(var2))
# complex (complex): complex numbers are square root of negative numbers
# square root of -25 = 5i = 5j
var1 = 5j
print(type(var1))
## Operations
#Arithematics operations (maths op)
#Relational operations
#logical operations (and/or/not)